If you want to keep your computer clock perfectly in sync for digital modes like FT8, try these tools for Windows or Linux. Meinberg NTP and Chrony can use data from multiple sources to keep your clock precisely synchronized.
Windows 🖥️
Meinberg NTP is an excellent free time synchronization software for Windows. It’s super lightweight, consuming only 1 MB of RAM!
In the installer, check Create an initial configuration file with the following settings: and select your country from the dropdown menu.
You can customize the config file if you want to add your own list of servers.
I suggest using the NTP Pool
You can find many quality public time servers from this list:
Github:
mutin-sa/Public_Time_Servers.md
To edit the server list, run Edit NTP Configuration as Administrator
server 0.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 6 maxpoll 7
server 1.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 6 maxpoll 7
server 2.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 6 maxpoll 7
server 3.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 6 maxpoll 7
Then run Restart NTP Service as Administrator to apply your settings
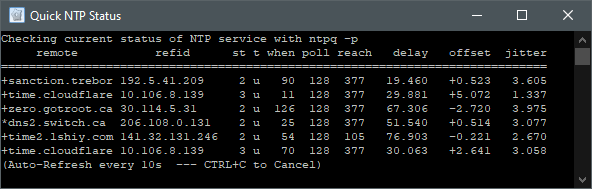
Run Quick NTP Status to view your connections:
Linux 🖥️
Chrony is a high accuracy and very flexible implementation of Network Time Protocol (NTP). Chrony can work with an intermittent network connection, and can be used with external GPS devices. Very useful if you need to run FT8 portable!
Installation
# Debian/Ubuntu:
apt install chrony
# Arch
pacman -S chrony
# Rocky/Alma/Fedora
dnf install chrony
Configuration
You can customize the config file to add your own list of servers. I suggest using the NTP Pool.
You can find many quality public time servers from this list:
Github:
mutin-sa/Public_Time_Servers.md
/etc/chrony/chrony.conf
pool pool.ntp.org iburst
Then restart Chrony
sudo systemctl restart chrony
To view your connections run chronyc sources -v
$ chronyc sources -v
210 Number of sources = 5
.-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
/ .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
|| | | \
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^- 0.ca.pool.ntp.org 3 10 377 805 -4085us[-4085us] +/- 40ms
^- 1.ca.pool.ntp.org 2 10 377 806 -1674us[-1674us] +/- 45ms
^- 2.ca.pool.ntp.org 2 10 377 24m -4359us[-4359us] +/- 57ms
^* 3.ca.pool.ntp.org 2 10 377 45m -4140us[-4083us] +/- 13ms
To check if your computer is synchronized, run chronyc tracking
$ chronyc tracking
Stratum : 2
Ref time (UTC) : Fri Mar 18 19:43:43 2022
System time : 0.000277688 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : +0.000283455 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000479173 seconds
Frequency : 64.315 ppm fast
Residual freq : +0.004 ppm
Skew : 0.241 ppm
Root delay : 0.010316090 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.000191347 seconds
Update interval : 258.0 seconds
Leap status : Normal
Done 😁
Congratulations, now you can run FT8 in perfect sync!
Check your accuracy on Time.is 🕒
